The Paint Bucket Tool is one of the most straightforward, yet helpful tools in Photoshop to fill selections, objects, or layers with color. Without needing to remember keyboard shortcuts, this tool makes filling anything with a color a breeze, along with opening doors to fill objects with a pattern too.
To use the Paint Bucket Tool in Photoshop, select it from the Toolbar where it is found beneath the Gradient Tool (G). In the Options Bar, set the Mode to Color or Pattern depending on what you want to fill your layer with. Now to fill a selection or layer, simply click in the area you’d like to fill.
Now, this just touches the tip of the iceberg in terms of understanding the settings related to this tool. Luckily everything you need to know to gain an in-depth understanding of this tool will be found in this tutorial.
What Is The Paint Bucket Tool In Photoshop?
The paint bucket tool allows you to fill layers, objects, and graphics with a specific color or pattern. Thanks to its many settings, you can color anything in Photoshop with precision and speed. This tool adds a color — the foreground color set in the document — to an area you select as well as the adjacent pixels around the selected point.
The Paint Bucket Tool is a great solution to quickly add color to large sections rather than using the Brush Tool to paint in the color.
How To Access The Paint Bucket Tool
You can find the Paint Bucket Tool in the toolbar under the gradient tool. To enable it, right-click the gradient tool. Then, select the paint bucket tool from the options listed.
Alternatively, press G to activate the paint bucket tool. If it doesn’t appear, press Shift + G to cycle through the options under the gradient tool menu and select the paint bucket tool.
The Paint Bucket Tool Settings Explained
Once you enable the paint bucket tool, some settings will appear in the Options bar for you to adjust.

Every setting you adjust makes the paint bucket tool behave differently, affecting the area you fill. I will show you what each setting does and how they affect the paint bucket tool.
The foreground/pattern drop-down menu allows you to set the source of the fill area. You can choose between filling areas with the foreground color or with a pattern.


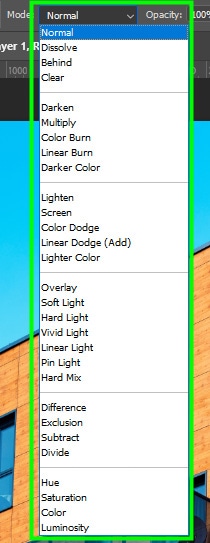
Mode controls how the color used to fill an area interacts with the layer you paint.

There are several Blend Modes available, and each one of them gives the areas you paint a different look. Some effects are only possible if you choose the right blend mode.


Opacity controls the transparency of the color used to fill an area.



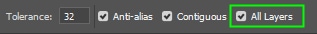
Tolerance controls the range of colors affected by the paint bucket tool. If you set tolerance to zero, only a specific pixel color is affected; if you increase Tolerance, you can paint more pixels.
If you use the paint bucket tool on an empty layer, it will fill that entire area, regardless of the value you set for Tolerance because there will be no variation of colors. That makes the paint bucket tool one of the best tools to fill empty layers.



Anti-Alias slightly blurs the edges of your selection, making them look smoother. Keep this setting checked to prevent problems such as jagged or rough edges.
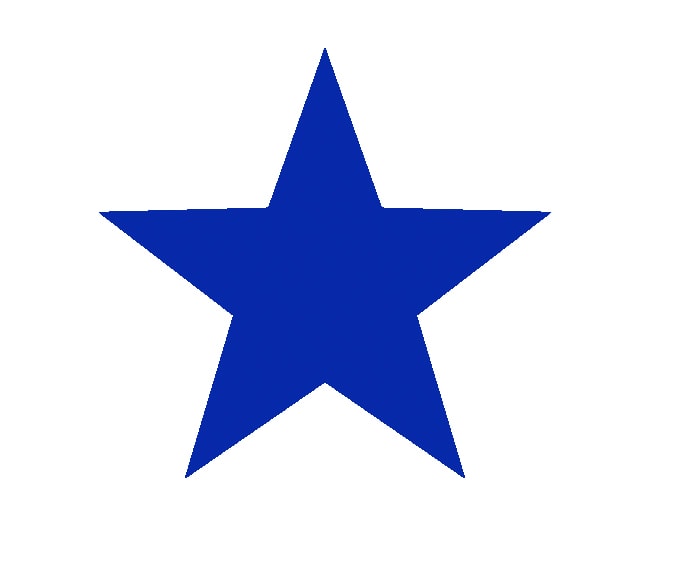
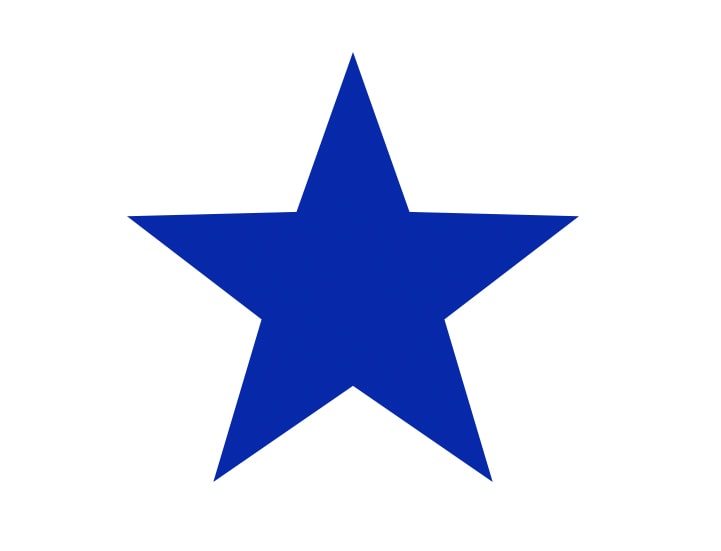
In the example below, you can see two stars I drew. For the star on the left, I unchecked Anti-alias, and for the star on the right, I left Anti-alias checked. See the difference in the edges of the object.
Contiguous restricts the area affected by the paint bucket tool.
Only pixels close to each other are painted when you enable this option. The paint bucket tool will change the colors of pixels across an entire layer if you uncheck this option.


All Layers allows you to expand the painted area to all layers in the Layers panel. As a result, when working with two or more layers, you can paint both layers simultaneously instead of painting one layer after another.
How To Use The Paint Bucket Tool
Now that you know how the paint bucket tool works, I will show you how to use this tool to change the color of any object in Photoshop.
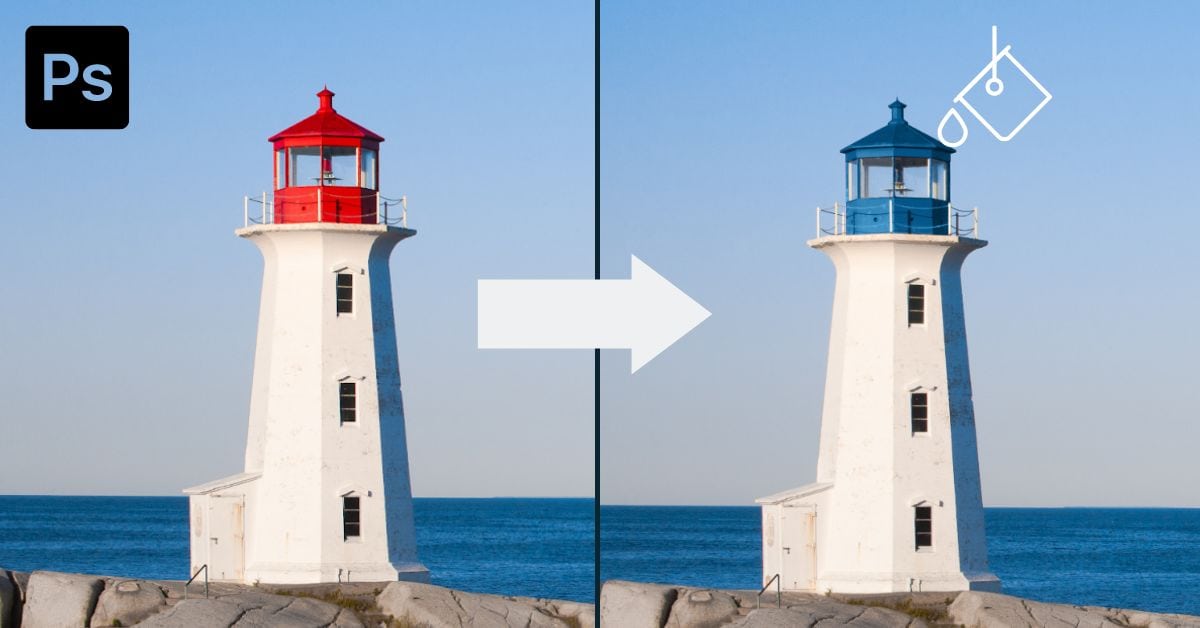
First, decide what area of your image you want to change the color of. In my case, that was the red area on the top of the lighthouse in the image below.
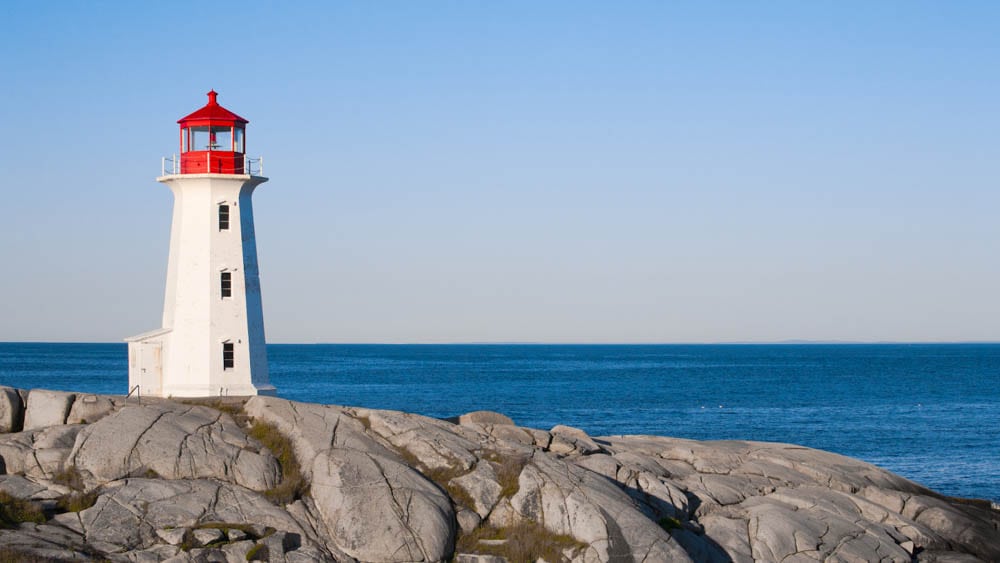

Now, go to the Layers panel and create a new layer by clicking the plus sign icon at the bottom of the panel.
The changes in the object’s color will be placed on that layer. You can apply the paint bucket tool to an image layer directly, but this makes it harder to make changes to the new color applied.
Now, keep the new layer selected and click the Rectangular Marquee Tool in the toolbar (M).

Next, drag around the object to create a selection. It doesn’t need to be a precise selection. The key here is to delimit the area to be painted so that you don’t risk affecting other regions if, for example, you accidentally set Tolerance to a very high value.
It’s not mandatory to select an object if you are using the paint bucket tool to change its colors. That’s because the Tolerance option usually allows you to precisely change the colors of objects, preventing the surrounding areas of it from being colored. However, it’s best if you at least isolate the object you are painting.
Ensure that the entire object is placed inside the selection and that no part of it is left out.
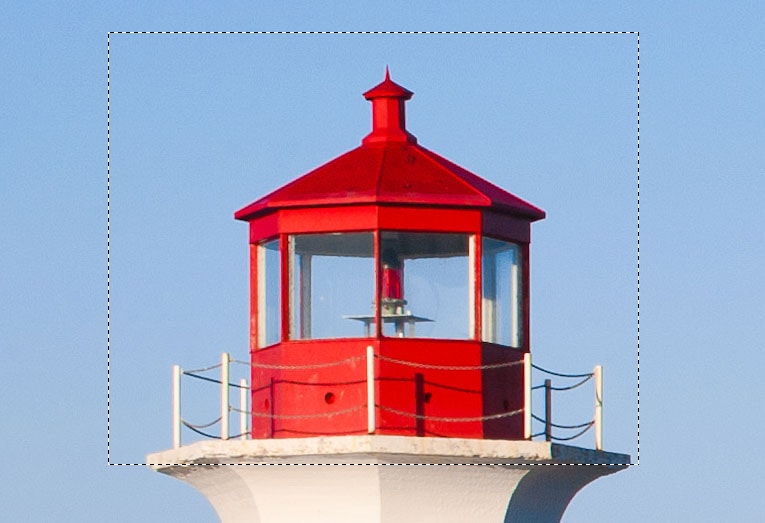

After that, select the Paint Bucket Tool in the toolbar (G).

Then, go to the Options bar and change the following settings:
- Source to Foreground
- Mode to Normal
- Opacity to 100%

Try to set Tolerance to a value that covers the entire object or at least the most part of it.

The minimum value for Tolerance is zero, and the maximum is 255. In my case, I set the Tolerance to 150 since the area I wanted to cover consists primarily of red and variations of red. If you are covering an area with a more uniform color, you will need a lower value and if you are painting something with many variations of tones, set tolerance to a higher value.
Properly adjusting Tolerance gives you great control over what colors are changed. That way, you avoid painting the surroundings of an object, for example.
Now, check the Contiguous, Anti-Alias, and All Layers checkboxes. Contiguous restricts the area painted to pixels of the same tone and color that are close to each other. Anti-alias prevents problems such as jagged edges.
And you will absolutely need to check All Layers if you are painting with the paint bucket tool non-destructively since, in such a case, you are sampling colors from the original image but keeping color changes on a separate layer.

After adjusting all the necessary settings, choose a color to cover the target area. To do this, go to the color boxes at the bottom of the toolbar and double-click the foreground color swatch.

From the Color Picker panel, pick any color to paint your object.
Once you choose a color, click the area you want to paint with the paint bucket tool. The color you picked will cover your object.

The new color will be very opaque. To fix that, go to the Layers panel and change the Blend mode to Color.
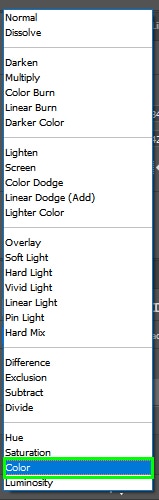
The Color blend mode preserves the luminance values of the original object and blends it with its new color. As a result, your object’s color will change, but its luminance values will remain the same, giving your object a more natural appearance since the shadows and lights are still there.
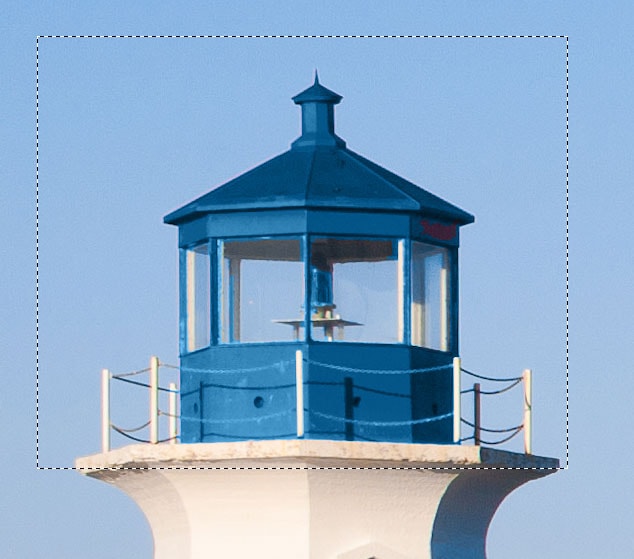

Changing the blend mode will also allow you to see the details of the painted area. If you think some areas are missing colors, decrease Tolerance and cover those areas.
For the area below, for example, I set Tolerance to 20px, and that was enough to fill the region that was left out.
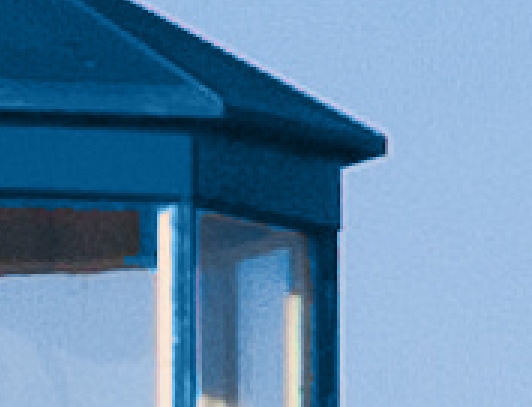


You can also use the Brush Tool (B) from the toolbar to cover the left-out area.
To use the brush tool, drag it over the area you want to paint. And if you think you painted too much, you can grab the Eraser Tool (E) and erase that extra color.

To use the eraser tool, drag it over the desired area.
Keep using the paint bucket tool, brush tool, and eraser tool (or combining these tools) until you feel that your object is well painted.