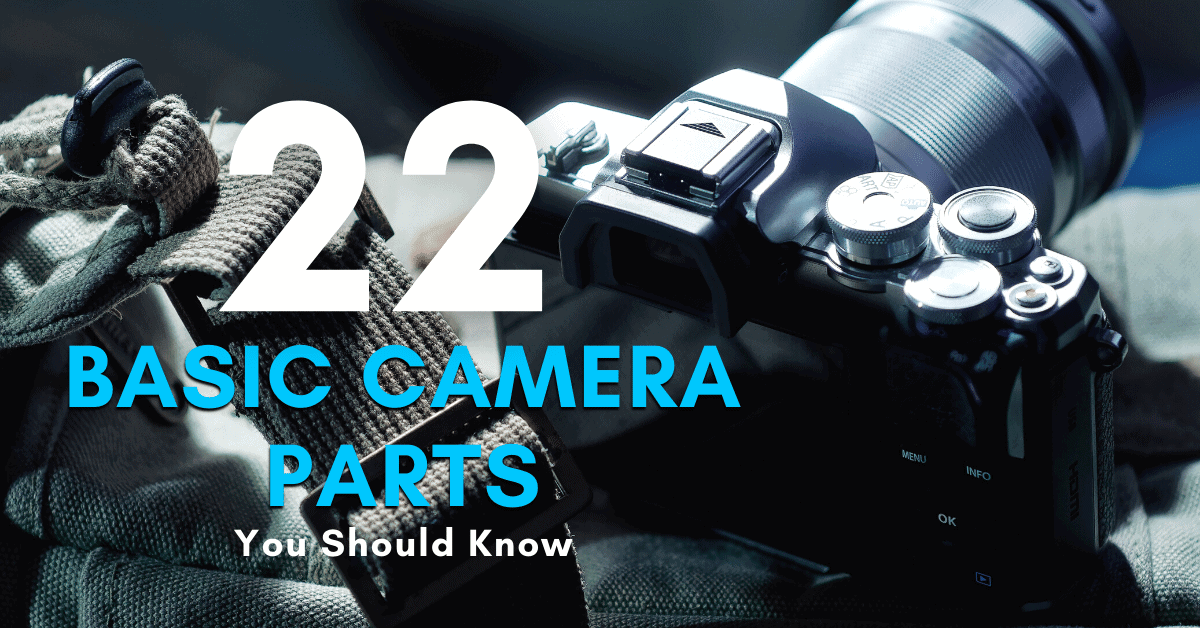
What Are The Basic Parts Of A Camera?
Let’s face it; there’s a lot going on when you look at a camera. With countless buttons, dials, switches, and settings, how are you supposed to keep track of it all? The easiest way to start feeling more comfortable with your camera is to understand its basic parts.
By breaking down the different sections of your camera into bite-size pieces, it’s easier to see it as a tool for creativity. No more feeling like cameras are some kind of complex mystery that you struggle to understand.
To help make it easy, I’ve broken down 21 basic camera parts that you should know. From the most basic parts to some lesser-known internal functions, this list has it all.
So no matter what brand of digital camera you’re shooting on, these parts still apply. Let’s get into it!
The Basic Parts Of A Camera
Although there is a long list of complex technology and moving parts in digital cameras, here are some of the most basic ones.
1. Camera Body
The camera body is what houses all the internal components of the camera. The easiest way to think of the camera body is everything, except the lens.
Camera bodies can come in a wide array of shapes, sizes, and weights, depending on the brand and purpose of the camera. For example, an action camera or compact camera could fit in your pocket. However, a DSLR camera can weigh 5+ lbs and need a dedicated bag to be stored in.
2. Lens
A lens is a barrel-shaped object that extends from your camera body. It’s filled with a series of glass elements that bend and focus light onto your sensor. Without a lens, you wouldn’t be able to capture anything with your camera. It’s what allows your camera to deal with incoming light and control the exposure of your photo.
There are many different types of lenses, and some lend better to certain types of photography. The main lens most beginners use is called a “kit lens” since it comes with the camera. It will have an adjustable zoom range, typically going from a wide-angle to a more mid-range focal length like 55mm.
As you develop your photography and realize the types of images you shoot, you can buy more specialty lenses. For example, if you love portrait photography, you might invest in a prime lens since it allows for more blurry backgrounds in your photos.
Depending on the type of camera you’re shooting with, lenses can be fixed directly to the camera body or be interchangeable.
3. Viewfinder
The viewfinder is the little window on your camera body that you can look through to frame your photo. By allowing you to see through your lens, you can get a good idea of how your photo will look before you take it.
On DSLR cameras, the viewfinder uses a series of mirrors to help you see what your lens sees. However, with Mirrorless cameras, you’ll have an Electronic Viewfinder (EVF), which has a digitally transmitted image to display in the viewfinder.
Regardless of DSLR or Mirrorless, the viewfinder serves the same basic purpose; to help you find the right focal length and composition before you take a picture.
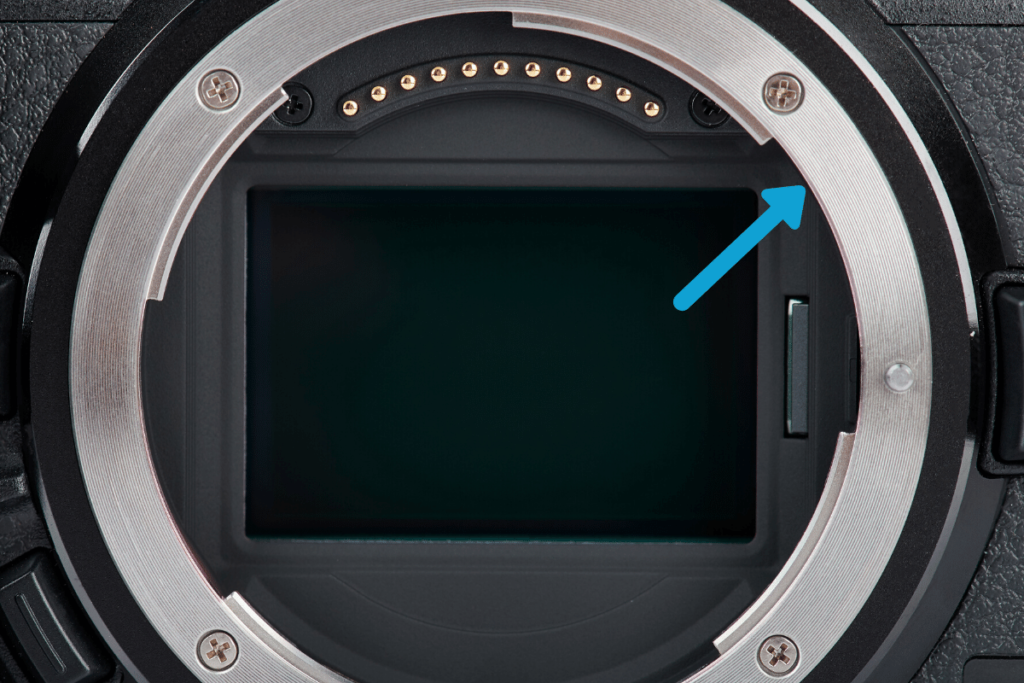
4. Sensor
The sensor is the single most important part of a camera since it’s responsible for recording light. You can find it in the middle of your camera body, directly behind the lens, as a small rectangle shape. The sensor records incoming light and turns it into an image to later save onto your memory card.
Different types of cameras can have different sized sensors, but the main purpose remains the same. With that said, a smaller sensor won’t be able to record as much information in your photo.
That’s why a full-frame camera typically takes higher quality images and performs better in low light than crop or micro 4/3 sensors.
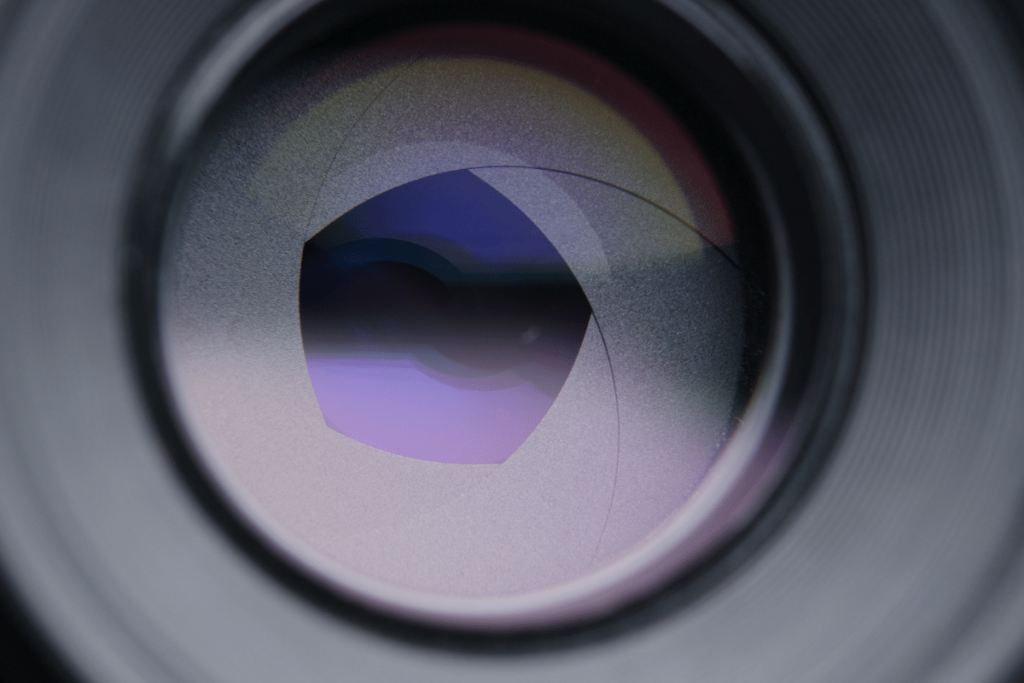
5. Aperture
The aperture is a donut-shaped ring inside of your lens that can expand or contract depending on the F-stop setting. With a wider aperture like F/4, you can allow more light into your camera to brighten your exposure. The opposite is true with a smaller aperture setting like F/16.
Aperture not only controls the brightness of your photos but also your depth of field. If you want to have a blurry background behind your subject, using a wider aperture will help you achieve that.
You can learn more about aperture and how it affects your photos here.
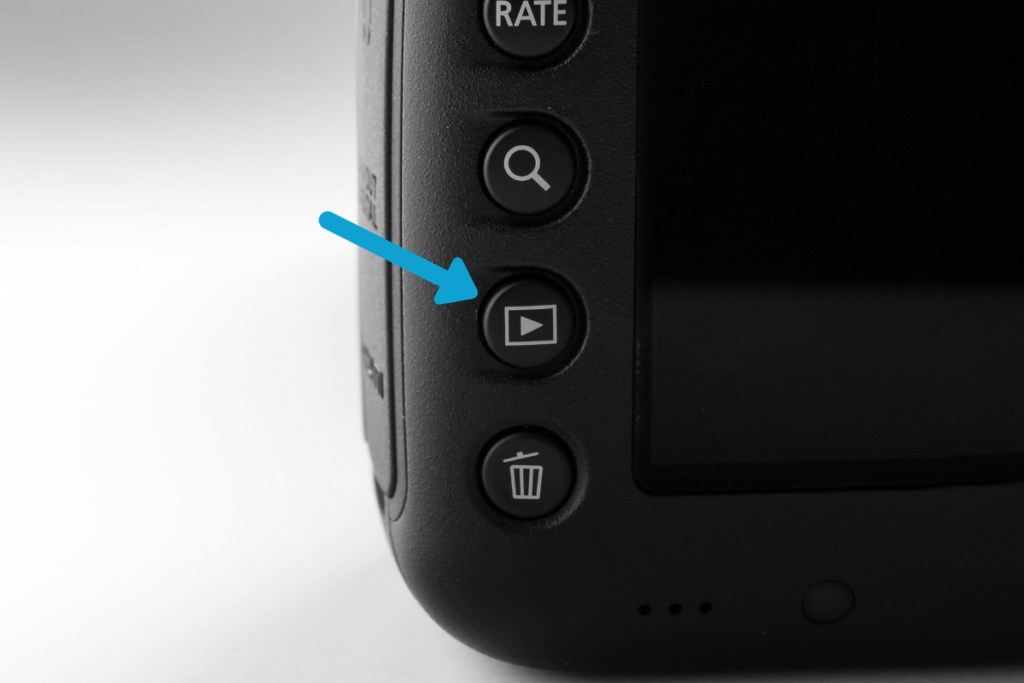
6. Playback Button
After you take a picture, you can review it with the playback button. Across Canon, Sony, and Nikon cameras, the icon is the same green box with the play button insider.
By pressing the playback button, you can look at your most recent photos or browse other media that’s saved on your memory card.
7. Shutter Release Button
The shutter release is the button you press to take a picture. When you press this button, you send a signal to open the shutter based on your preset shutter speed. The shutter will then open and close, allowing light to reach your sensor and record an image onto your memory card.
Although the shutter release button is very straightforward, choosing your shutter speed can be challenging. Depending on if you want to freeze motion or capture a long exposure, the correct settings will change. To help get you started with shutter speed, check out this guide.
8. LCD Screen
The LCD is the screen on the back of all digital cameras. This screen can display everything from your current camera settings to your recently captured photos and video.
In recent years the LCD has become increasingly popular for Live View. This mode lets you see what your camera sees directly on your LCD. This replaces the need for a viewfinder and has become a favorable option for many photographers.
Especially so because you can preview your settings before you actually take a picture.
On many cameras, the LCD screen is fixed in place, while others will have a flip-out screen. Especially when you’re shooting at awkward angles or close to the ground, swivel screens make all the difference.
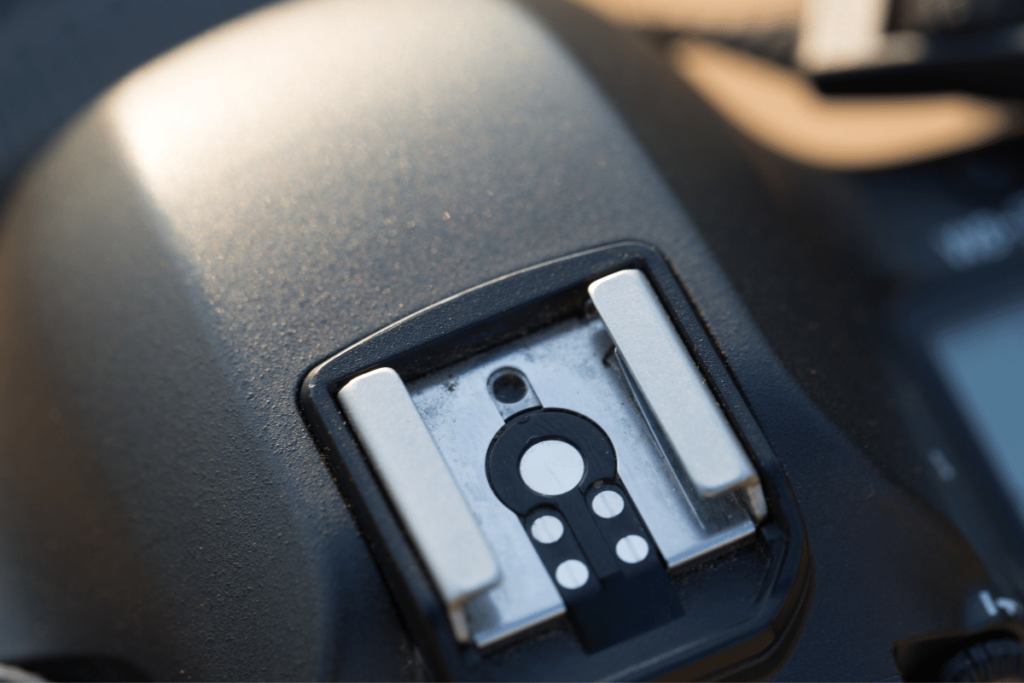
9. Hotshoe
The hotshoe is a metal bracket found on top of most DSLR and mirrorless cameras. It’s used to mount and connect external devices such as a flash or flash remote directly to your camera. With small sensors at the bottom of this bracket, your camera can send signals to your external accessories mounted to the hot shoe.
That’s why when you press the shutter, your external flash will fire, for example.
Most compact cameras do not have a hotshoe, or have a miniature version of one. In some cases, a camera will have what’s known as a “coldshoe” which allows you to mount accessories without transmitting a signal to them. A coldshoe just doesn’t have the same sensors that a hotshoe does.
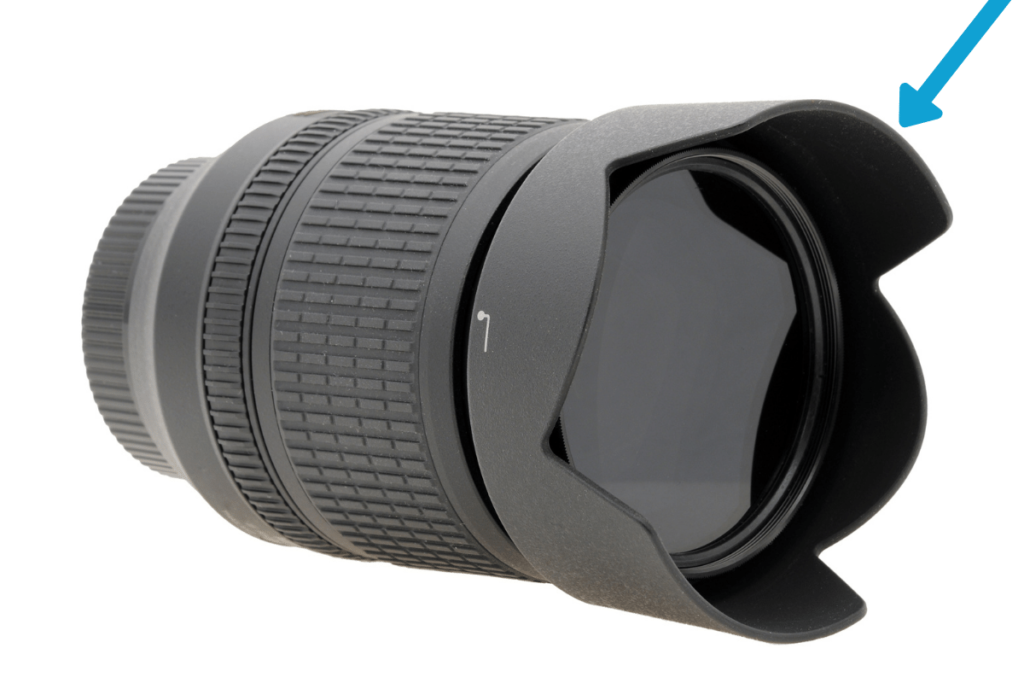
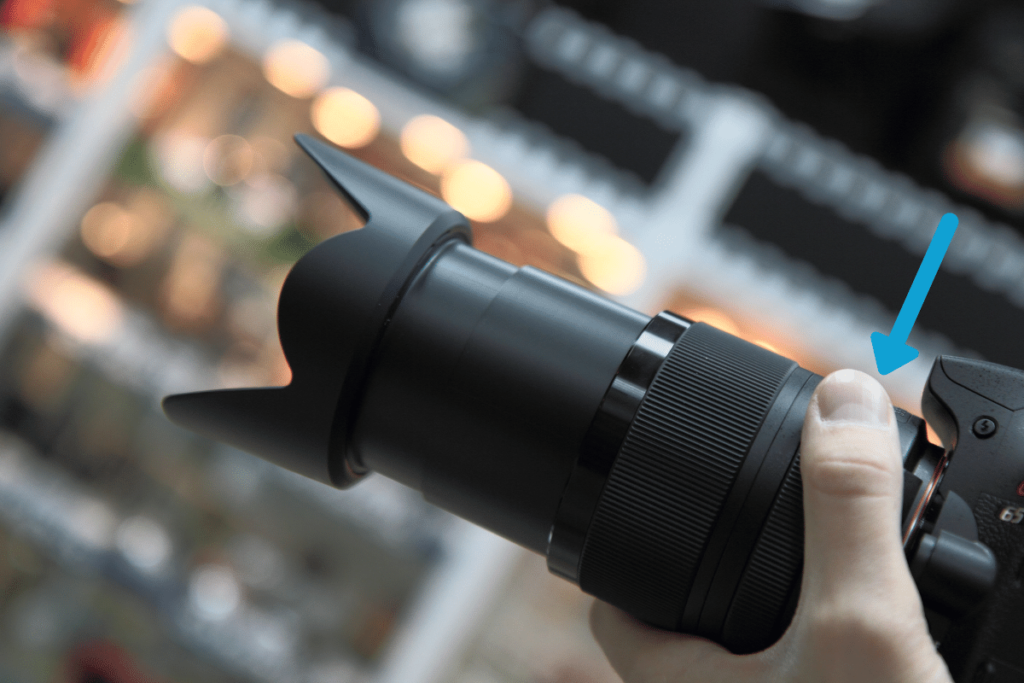
10. Lens Hood
A lens hood is a removable plastic ring that can extend from the front of certain lenses. It’s used to help shield your lens from flaring and also serve as protection from an accidental bump.
Not all lenses will have a lens hood available, particularly so with compact cameras or wide-angle lenses. Since they extend around your lens element, they can cause problems at wider focal lengths. That’s why it’s more common to see zoom lenses with large lens hoods. Since there’s a more narrow field of view, the lens hood can’t be seen.
To learn more about the advantage of using a lens hood, check out this post.
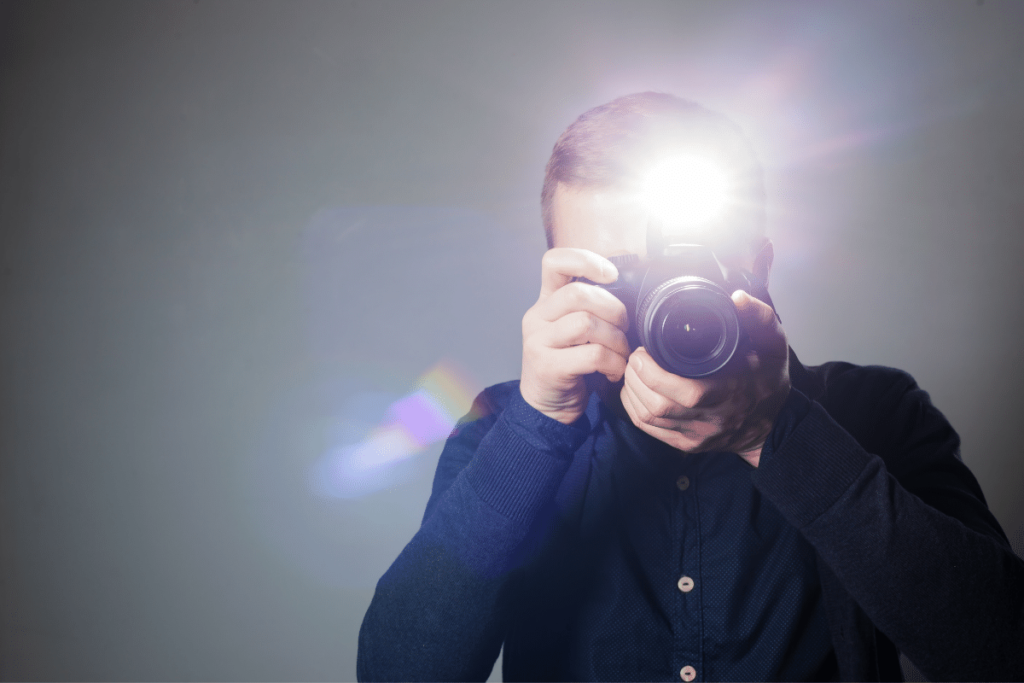
11. Flash
Some digital cameras will have a flash built into the top of the camera body. By engaging the flash settings on your camera, it will pop up and active when you press the shutter release.
A flash is an easy way to get more light into your scene, especially when shooting in low light. The problem is that on-camera flashes don’t always create the most flattering images.
Since the lights shining directly from your camera, it can end up casting harsh shadows on your subject while washing out the colors.
Although it’s not the greatest to use in every situation, it can be a useful tool to have built into your camera. On-camera flashes are most commonly found in entry-level DSLR cameras.
12. Flange
The flange is the bracket/hole that connects your lens to the camera body. This is only something you’ll find on cameras with interchangeable lenses.
On the flange, there are several markings to help your lens mount properly into place. Once mounted, the contact pins and locking mechanisms will align between your lens and the camera body. That way, you can control your lens via your camera’s settings.
Without a flange, you wouldn’t be able to mount your lens or have access to autofocus.
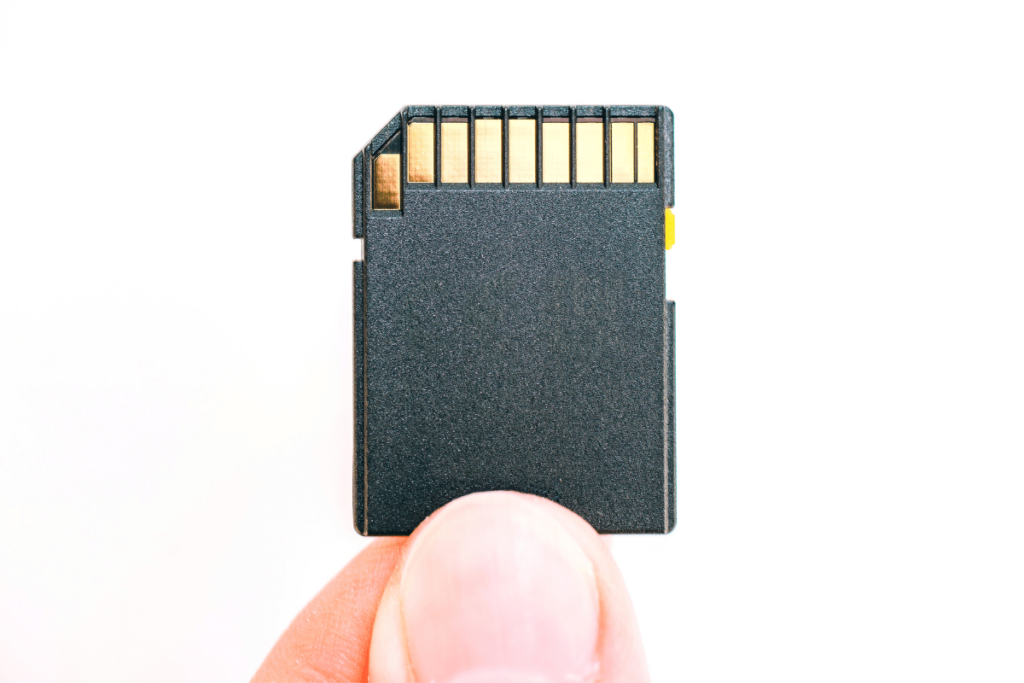
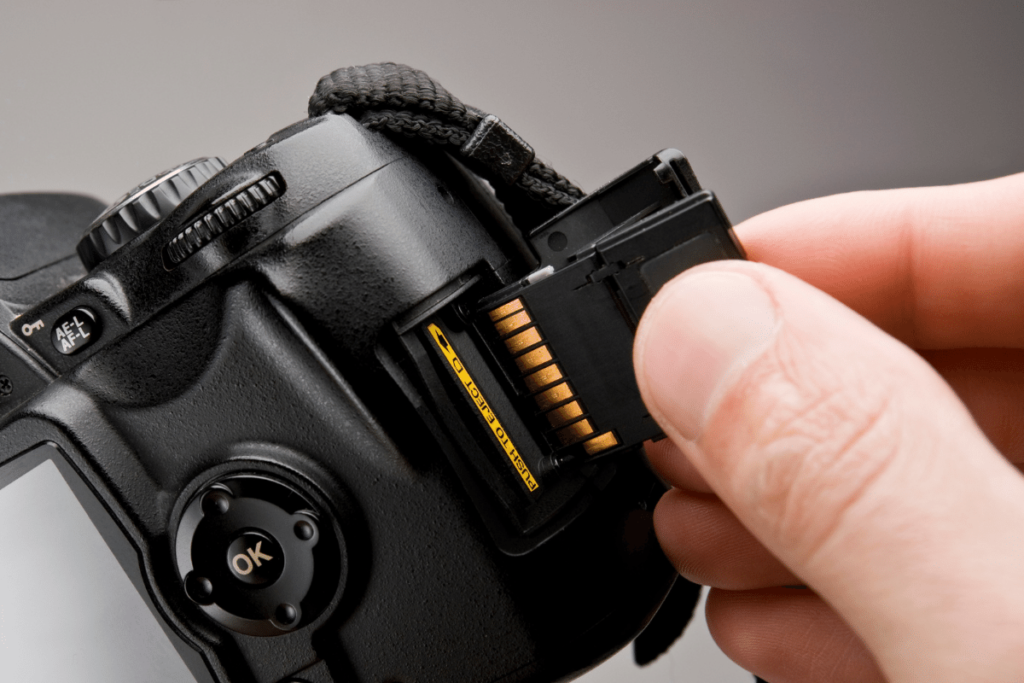
13. Memory Card
The memory card is another basic camera part that’s essential to the whole operation. After all, if you don’t have anything to save your images onto, then what’s the point of taking pictures?
Different cameras require different memory card based on a variety of reasons. A few of them being the file size your camera shoots, the size of your camera, and whether it’s designed for photo or video purposes.
14. Memory Card Slot
In order to send information for your camera to a memory card, you need to use a memory card slot. Built into all digital cameras is a dedicated spot for your memory card to be stored.
In some professional cameras, there will be multiple card slots so you can backup data while you’re shooting photos. This offers some much-needed peace of mind when you’re shooting for a client. In case one card happens to fail, you always have a backup option to work with.
Depending on the type of camera, the card slots will vary to fit a certain type of card. Whether it be Micro SD, SD, or CF cards, every camera and camera brand has its own way of doing things.
You can find the memory card slot located somewhere along the side of the camera body, often beside the camera grip.
15. AF & MF Switch
On most modern lenses, you’ll see a switch labeled AF/MF, which stands for Autofocus (AF) and Manual Focus (MF). By moving this switch, you can change which mode your camera uses to focus.
In autofocus mode, your camera will automatically pick the focus based on your autofocus point. This makes life a lot easier when you’re shooting action shots or portrait photos, for example.
Manual focus mode, on the other hand, requires you to manually set the focus by turning the focus ring on your lens. For close up shots or when your autofocus isn’t doing what you want, manual focus is always there to save the day.
To learn more about which focus mode, you should use for your photography, check out this post.
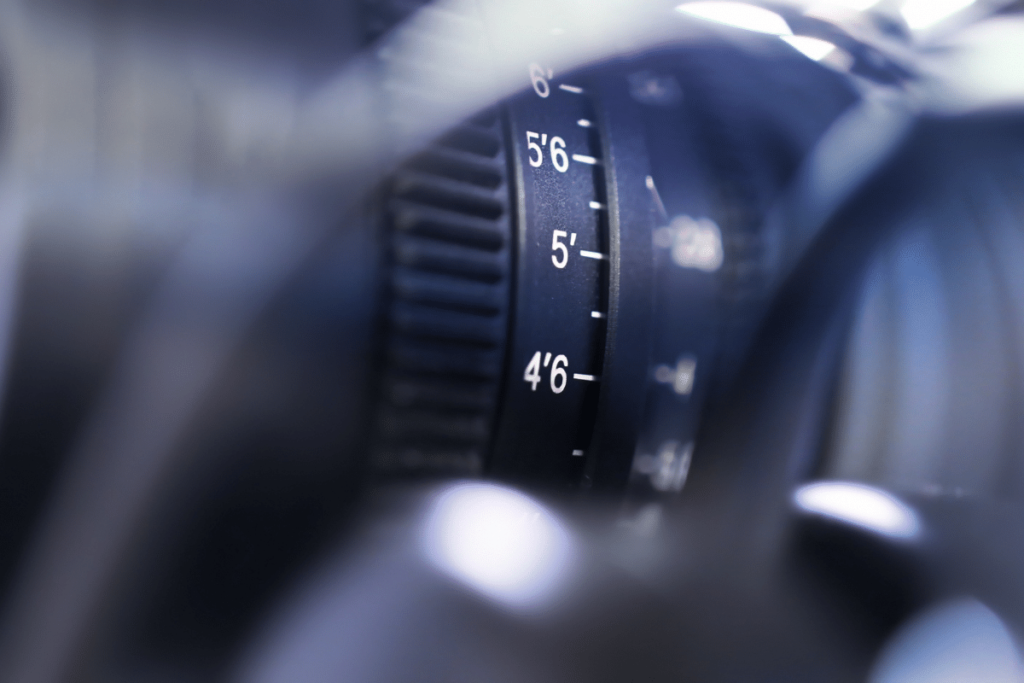
16. Focus Ring
The focus ring is found near the front of your lens and is what controls your focal point while using manual focus. By turning your focus ring, you can change what parts of your image are in focus. There is also a distance marker located somewhere along the lens to help you identify how far away your focus plane will be.
While you’re using autofocus, the focus ring becomes inactive since your camera has taken over. In order for the focus ring to actually change your focus, you must be using manual focus.
17. Zoom Ring
On zoom lenses, the zoom ring changes how zoomed in your photos appear. By shifting the physical distance between the glass elements inside the lens barrel, your camera’s field of view is changed.
The zoom ring is typically the one closest to your camera body. By rotating it left or right, you can find change your focal length based on the markings on your lens.
You’ll find a zoom ring on every lens except for prime lenses since they have a fixed focal length.
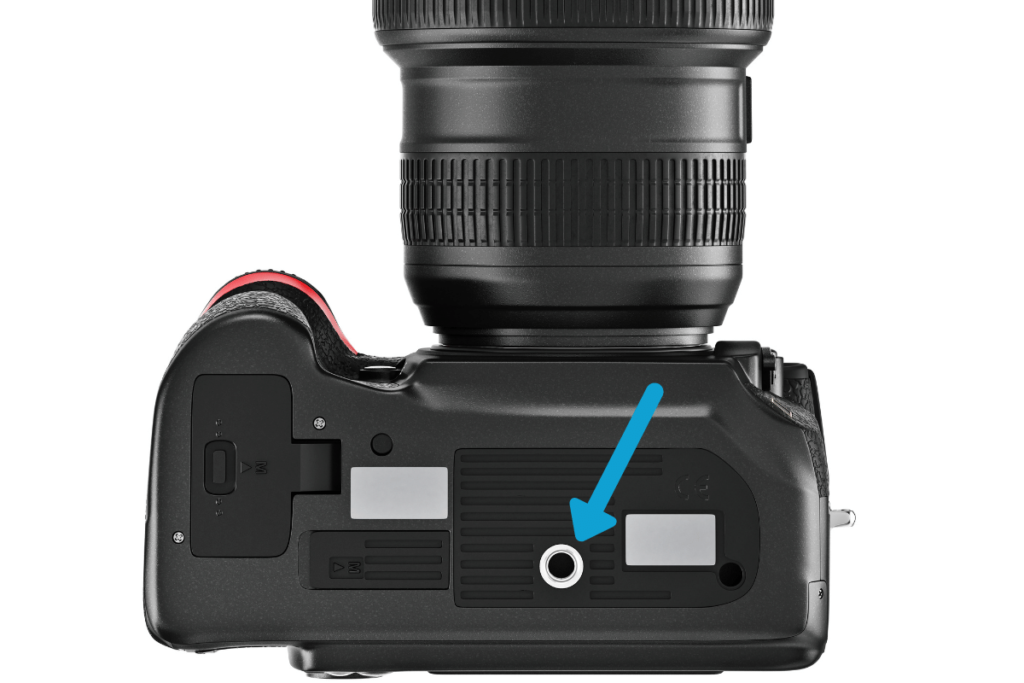
18. Baseplate Reciever
Found on the bottom of your camera is a 1/4″ or 3/8″ female thread called the baseplate receiver. This is meant for mounting tripod baseplates so you can attach your camera onto a tripod head. By screwing a quick release plate into this female receiver, you can securely mount your camera to a tripod with ease.
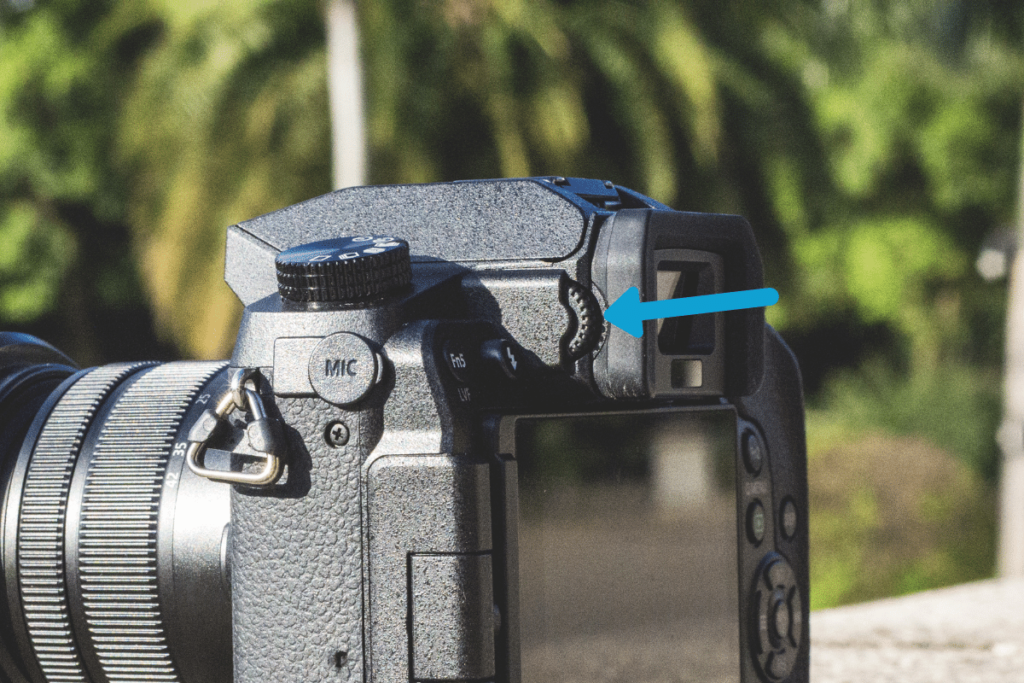
19. The Diopter
On many cameras, particularly Canon and Nikon, you’ll find a small dial beside the viewfinder called the diopter adjustment. Depending on your eyesight, you might have a hard time focusing your vision when looking through a viewfinder. By adjusting the diopter, you can help ensure you see the image clearly.
Simply by adjusting the magnification of your viewfinder, the diopter helps correct the image to suit your vision needs.
20. User Controls
The user controls are all of the buttons found on your camera. With options to change menu settings, camera settings, or shooting modes, these buttons control how your camera operates.
Although every model of camera will have slightly different user controls, they are often in similar locations. For example, the mode dial is always located on the top of the camera near the viewfinder. The shutter release is always at the top of the camera grip. Although different cameras can vary, once you understand one camera, it’s easier to figure out other models as well.
21. Camera Strap
The camera strap tethers directly to your camera, making it easy to carry around without the fear of dropping it. Typically meant for slinging your camera around your neck, the camera strap is an easy way to keep your camera secure while having it out of your camera bag.
Camera straps mount onto a camera body directly via two dedicated strap loops on the body. By threading each end of the camera strap through the loops, your camera is securely attached to the strap.
22. Auxiliary Inputs
Along the side of most digital cameras, opposite to the memory card slot, is an array of auxiliary inputs. Things such as remote trigger input, microphone inputs, or even HDMI options for tethering your camera to a computer.
Some cameras will have more input options than others, especially so with video cameras. Ultimately these ports are meant for additional accessories to help improve or alter the way you shoot.
What Are The Five Basic Parts Of All Cameras?
No matter what brand of camera you’re using, there are 5 basic parts that all cameras have.
The five basic parts of all cameras are the camera body, lens, sensor, shutter, and aperture. Together, these make up the most basic components of any camera. Without them, it would be impossible to capture pictures or control the brightness of your exposure.
From digital to film cameras, these five parts are all the same.
How To Start Learning More About Your Camera
Now that you know the basic parts of a camera, it’s time to start taking photos! The first barrier many people face is feeling intimidated and not knowing where to begin. With so many settings, it might seem hard to see your camera as a creative tool rather than a complicated piece of tech.
The thing is, when you really break it down, a camera is just a box with a recording plane (aka the sensor). Everything else works to manipulate the amount of light that can reach the sensor to alter how your final photo appears.
If you’re just getting started in photography and want to get going on the right foot, make sure to check out this complete guide to learning photography.
Or download my FREE 12-Week Photography Blueprint and start taking your skills to new levels, with an actionable step-by-step process.
Happy Shooting,
– Brendan 🙂